1. PMAnti-photodamage 100 Overview
Skin photodamage is a range of skin reactions and disorders caused by ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight and other forms of light exposure that not only lead to skin aging and aesthetic problems, but can also lead to serious health problems, including sunburn, tanning, photoaging, rosacea, sensitive skin, hyperpigmentation disorders, and photocarcinogenesis. Ultraviolet light is one of the main causes of skin photodamage. Therefore, Plamed develop PMAnti-photodamage®100, it’s a natural mixture of Scutellaria Baicalensis Root Extract, and Sophora Japonica Flower Extract. The actives are bacalin and rutin, both of them have anti-inflammatory, sun-protect effects for skin care.

| Product name | PMAnti-photodamage®100 |
| INCI name | SCUTELLARIA BAICALENSIS ROOT EXTRACT, SOPHORA JAPONICA FLOWER EXTRACT,
HYDROXYPROPYL CYCLODEXTRIN |
| Actives | Baicalin≥2%, Rutin≥1% |
| Solubility | Water-soluble |
| Dosage | 0.1%~2% |
| Function | Anti-photodamage |
| Highlight★ | Block UV + reduce skin photodamage = comprehensive anti-pthotodamage |
2. PMAnti-photodamage®100 Botanical Source
The dried root of scutellaria baicalensis has been used by the Chinese as a traditional medicine for more than 2,000 years and is now officially listed in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. The main active ingredient in Scutellaria baicalensis are flavonoids, of which baicalin has the highest content. Scutellaria baicalensis root extract is widely used in anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory cosmetics, and it can also be used as whitening, sunscreen and anti-aging cosmetic additive.
Sophora extract is a natural plant ingredient extracted from Sophora japonica flowers, and the main components include flavonoids, isoflavones, saponins and so on. Sophora japonica not only has ornamental value, but its flowers and buds are also widely used in food, medicine and cosmetics. It is a common Chinese herbal medicine with the effects of clearing heat and detoxification, cooling the blood and stopping bleeding. It is often used in cosmetics for its antioxidant, whitening and anti-inflammatory effects.

3. PMAnti-photodamage®100 Mechanism
- Mechanism of UV damage to skin
- Oxidative stress response damage: UV radiation causes the skin to produce excessive amounts of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), and apoptosis will be activated to prevent cellular damage from ROS, resulting in oxidative stress. Oxidative stress can lead to inflammatory reactions such as erythema and edema, as well as sunburn, photoaging and even tumors.
- Photoaging damage: Upon UV irradiation, UVA and UVB induce ROS production, abnormal matrix degradation, free radicals and mitochondrial mutations, and immunosuppression, respectively, which further promotes the expression of matrix proteases (MMPs), which degrade collagen and elastin fibers, ultimately leading to photoaging.
- Skin inflammation: UV radiation promotes the release of inflammatory mediators such as skin 5-hydroxytryptamine, kinin release and induces the expression of activated nuclear transcription factors AP-1 and NF-κB, whose activation leads to inflammation.
- Skin DNA damage: UVB can cause oxidative DNA damage not only indirectly by inducing ROS, but also directly to the DNA of skin keratin-forming cells. Nucleic acids, proteins, trans-uronic acid, melanin and their precursors in the skin are able to absorb UVB and directly cause DNA damage and other biological tissue damage.
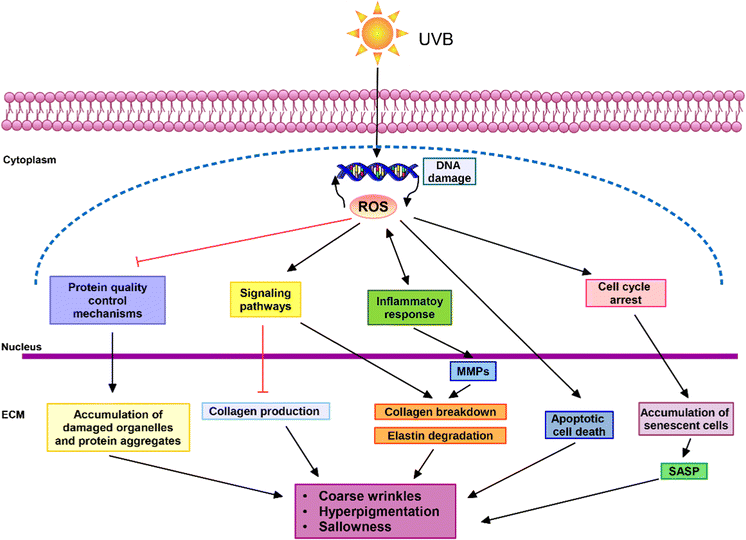
- Mechanism of anti-photodamage
According to the above mechanism of photodamage to the skin, the pathway for reducing photodamage to the skin includes isolating the radiant light source from the skin or reducing the damage to the skin from the radiant light source through certain signaling pathways in the skin.
- Mechanism of light absorption or reflection: By relying on the light absorption or light reflection of substances to filter harmful light sources, reducing the amount of exposure to harmful light sources in the skin to achieve anti-light damage efficacy.
- Mechanism of reducing damage of radiation light source to skin: Reduces skin DNA damage, scavenges excessive ROS in the skin, reduces loss of antioxidants in the skin, anti-photo-aging, inhibits inflammation and erythema (post-sunburn erythema is related to angiogenesis) and other photoprotective effects, enhances the skin’s ability to fight against UV rays, and reduces photodamage of the skin.
PMAnti-photodamage®100 (Baicalin and Rutin) can prevent skin from contacting with UV rays by absorbing most of the UV rays to isolate the UV rays. Meanwhile, it can enhance the skin’s ability to fight against UV rays by lowering the skin’s DNA damage, removing the skin’s excess of ROS, reducing the degradation of collagen, inhibiting inflammation and other photo-protective effects to reduce the skin’s photo-damage and photo-aging.
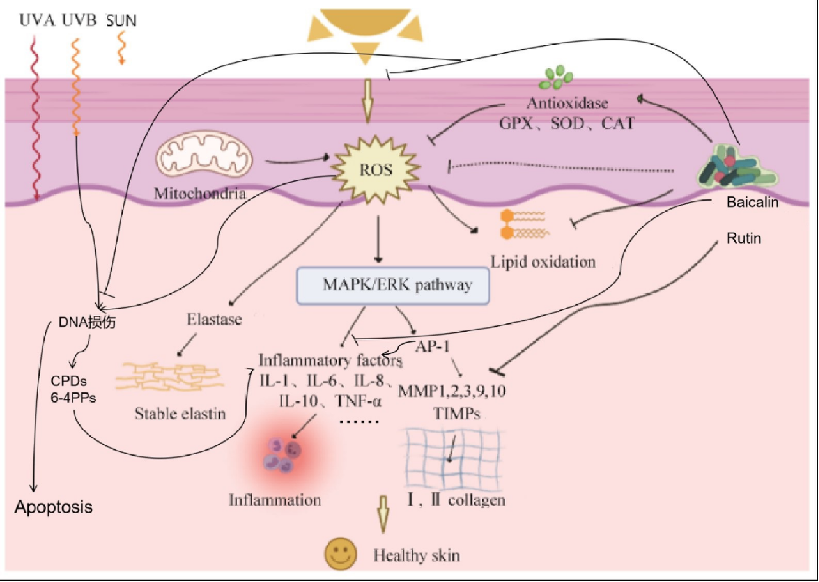
4. PMAnti-photodamage®100 Actives Efficacy
- Baicalin-Mechanism of light absorption or reflection
Baicalin is a non-toxic, harmless, broad-spectrum UV-protective substance with a strong UV-absorbing ability. There are two long conjugated systems in the molecular structure of baicalin, and there are two main absorption bands in the UV absorption spectrum, band I at 300 nm ~ 400 nm, band II at 250 nm ~ 290 nm, and there are strong absorption peaks at 242 nm, 271 nm, and 310 nm. Therefore, baicalin is able to absorb ultraviolet rays, such as UVA and UVB, especially the absorption of UVB, with an absorption rate of 80% [1-2]. In addition, some experiments have proved that Scutellaria baicalensis extract has the maximum absorbance at 310~350 nm, which further proves that baicalin has the effect of UV protection.
1. Anti-oxidation
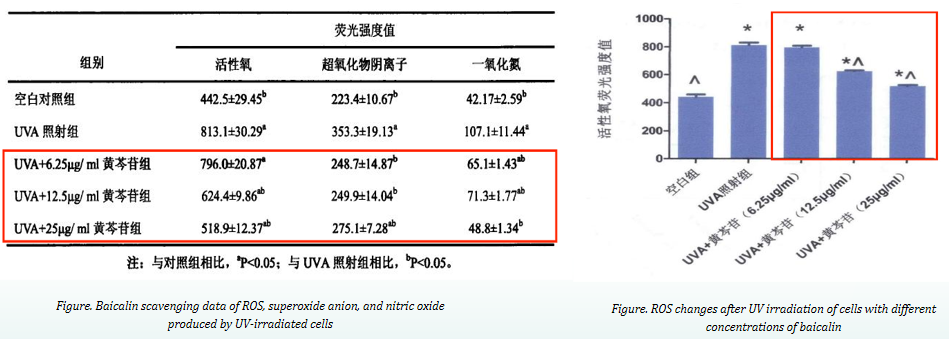
As can be seen from the above figures, baicalin can effectively scavenge all kinds of oxidation products (reactive oxygen species, superoxide anion, nitric oxide) and reduce the content of ROS. It can effectively prevent the cells from generating oxidative stress, equalize the level of oxidative and antioxidant capacity in the cells, and reduce the occurrence of cell apoptosis.
2. Anti-inflammation
Baicalin significantly inhibits the translocation of NF-κB to the nucleus, the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome (which promotes the synthesis of inflammatory factors IL-1β and IL-18), and the maturation of GSDMD (regulation of cellular inflammation), which ultimately inhibited UVB-induced apoptosis and attenuated skin damage. Through molecular docking, we found that baicalin has the potential to bind to NF-κB, NLRP3 and GSDMD.
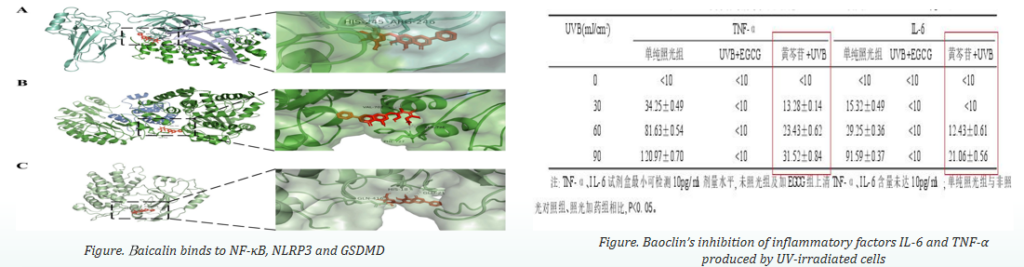
The left figure shows the simulated molecular docking of baicalin and NF-κB, NLRP3 and GSDMD, respectively, which indirectly indicates that baicalin has an obvious inhibitory effect on the secretion of the corresponding inflammatory factors. The right table is a direct analysis test of the inflammation secreted by the cells, which directly proves that baicalin has an obvious inhibition of the secretion of the inflammatory factors IL-6 and TNF-α, and both of them confirm the anti-inflammatory efficacy of baicalin.
3. Resist photoaging damage
As shown in the figure on the right, baicalin can inhibit the production of the aging-related proteins P53, P16, and P21, and thus alleviate the delayed cell proliferation, premature aging, and decreased collagen synthesis and increased degradation of skin fibroblasts caused by UVB radiation, and ultimately achieve the effect of anti-skin photo-aging.
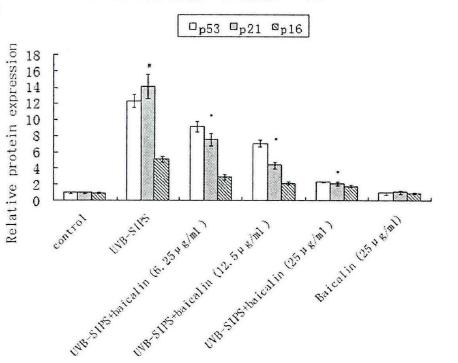
Figure. Baicalin can affect P53, P16, P21 of UV-irradiated cells
4. Reduce DNA damage
Baicalin can reduce the production or accelerate the clearance of CPDs (cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers, a form of DNA damage induced mainly by ultraviolet (UV) radiation), thereby reducing UV damage to DNA and reducing the inflammatory response caused by CPDs.
- Rutin-Mechanism of light absorption or reflection
Rutin can improve the UVA resistance of sunscreen products, and in combination with the UVA chemical sunscreens benzophenone-3 and butylmethoxydibenzoylmethane to enhance the photostability of these two sunscreens, and improve the antioxidant property as well as the sun protection index of their formulations [1-2]. Adding rutin to UVB sunscreens resulted in an increase in the critical wavelength of the formulations and enhanced UVA resistance, further confirming the ability of rutin to resist UVA [3]. It was demonstrated that rutin enhanced the sun protection index of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide compared to quercetin. When 10% rutin and 10% titanium dioxide were added to the formulation, the SPF (sun protection factor) was 34.29, and the PFA (Protection Factor of UVA) value was 16.25; when 10% rutin and 10% zinc oxide were added to the formulation, the SPF was 11.25, and the PFA value was 9.75 [4], which further proved that rutin has the ability to absorb part of the harmful light.
1. Anti-oxidation
Figure. Rutin inhibits ROS production in UV-irradiated cells (Rutin is the main component of Sophora japonica extract)
By applying rutin to the backs of hairless mice subjected to UVB radiation, the experimenters found that rutin could significantly reduce production of ROS and lipid peroxides induced by UVB, which in turn prevented the body from causing a series of oxidative stress reactions due to excessive ROS [1]. As shown, Sun Xuan et al. demonstrated that Sophora japonica extract (rutin) could inhibit excessive ROS production induced by UVA in the skin [2].
2. Anti-inflammation
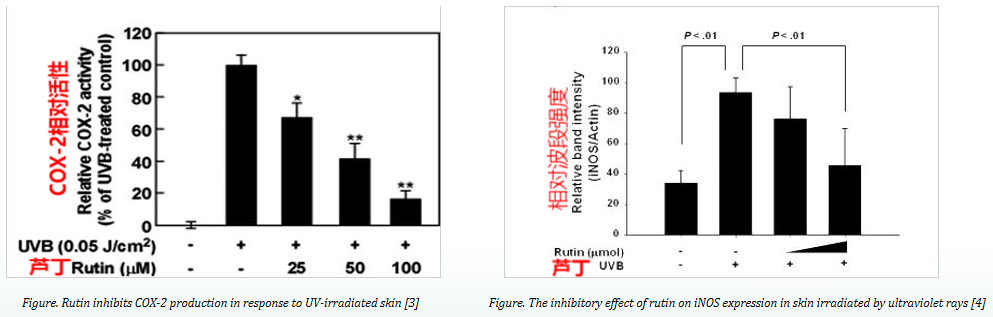
According to the above data, rutin inhibits the UVB-induced phosphorylation of ERK, MKK4/JNK, and MKK3/p38 signaling pathways, which leads to the down-regulation of COX-2 (cyclooxygenase-2) and inhibition of iNOS (nitric oxide synthase) expression [1, 3]. It has also been demonstrated that rutin can reduce the secretion of inflammatory factors TNF-α and IL-6 [2, 4], thus providing anti-inflammatory effects.
3. Resist photoaging damage
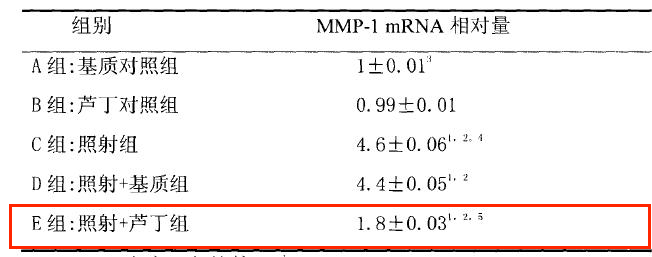
Figure.The inhibitory effect of rutin on the relative amount of MMP-1 mRNA in skin after ultraviolet irradiation [2]
Topical rutin cream has a certain protective effect against irradiation, which can significantly improve the appearance of UV-induced photoaging in mouse skin, reduce the increase of MDA content in mouse skin caused by UV irradiation to a certain extent, enhance the activity of antioxidant enzymes SOD and GSH-Px, and inhibit the increase of MMP-1 mRNA level.
4. Reduce DNA damage
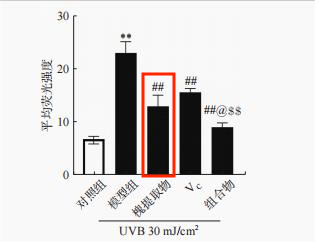
Figure. Inhibitory effect of Sophora sophora extract (Rutin) on CPDs in cells after ultraviolet irradiation [1]
Sophora japonica extract (rutin) significantly reduced the amount of CPDs (cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers, a form of DNA damage induced primarily by ultraviolet (UV) radiation) produced by UVB induction.
5. PMAnti-photodamage®100 Efficacy Tests
- UV full-band barrier test
The test measures the barrier of PMAnti-photodamage®100 in the full UV band (290 nm~400 nm) by means of the SPF-290AS instrument.
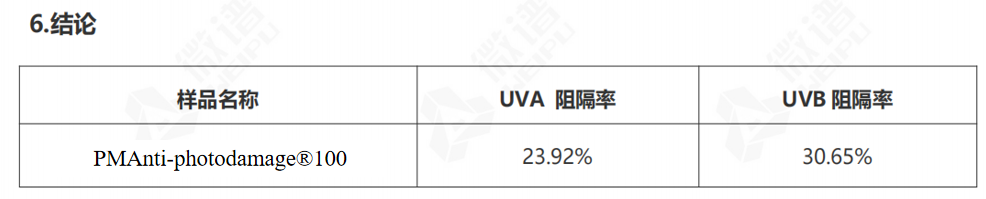
The sample PMAnti-photodamage®100 has a UVA blocking rate of 23.92% and a UVB blocking rate of 30.65% at 1% concentration. It indicates that PMAnti-photodamage®100 has the effect of blocking ultraviolet rays.
- Anti-photodamage effect based on zebrafish test
Zebrafish embryos are exposed to different test concentrations of PMAnti-photodamage®100 group, model control group and blank control group. After 1h exposure, 0.3J/cm2 UVB irradiation was used for modeling, and then replace with the corresponding solutions. After 24h of incubation, the fish embryos are photographed by microscope to measure the tail area and statistically analyze to evaluate the efficacy of the samples in preventing photodamage.
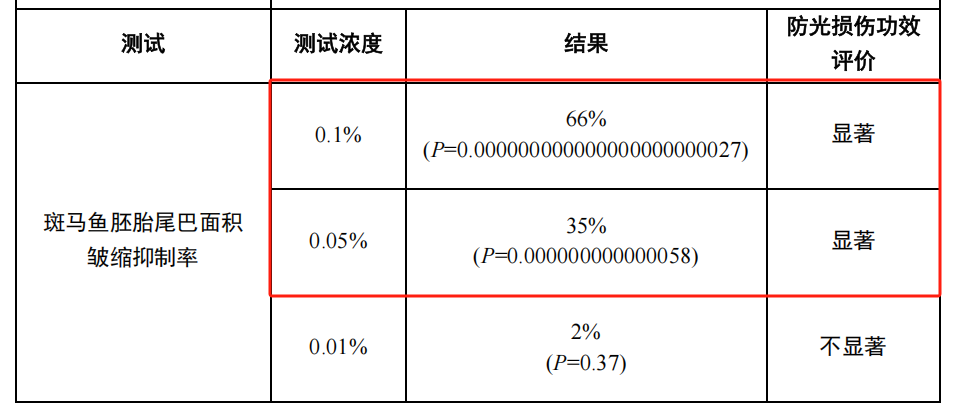
PMAnti-photodamage®100 can significantly attenuate zebrafish embryonic tail wrinkling induced by UVB irradiation at both 0.1% and 0.05% concentrations, with inhibition rates of 66% and 35%, respectively, and had an anti-photodamage effect.
6. PMAnti-photodamage®100 Advantages
- Plant natural source, good stability.
- Multi-target photodamage repair was carried out by synergistic action of multiple active substances.
- High safety, third party tests reports.
- Block ultraviolet rays and reduce skin damage.
7. PMAnti-photodamage®100 Safety
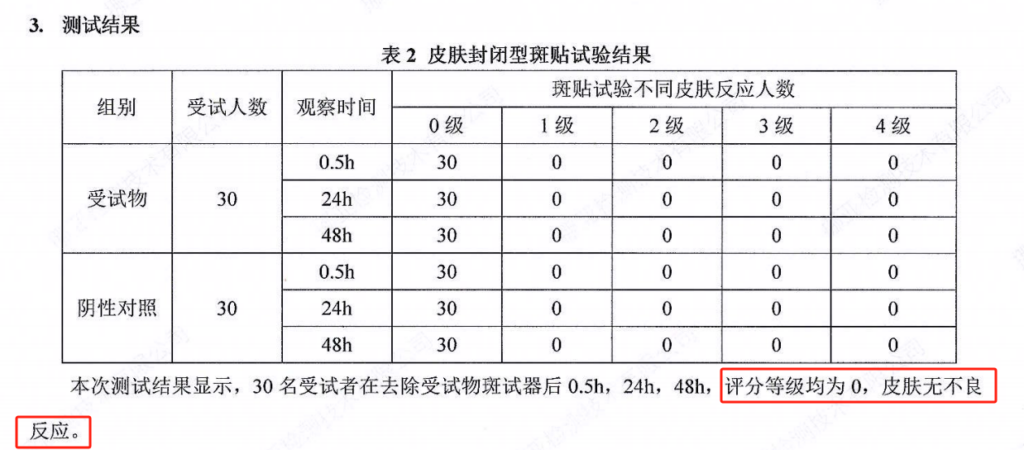
- Human skin patch test
According to the “Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmetics” (2015 edition), the safety test of 2.35% concentration of PMAnti-photodamage®100 showed that 30 people had no adverse skin reactions 48 hours after using the sample.
8. PMAnti-photodamage®100 Stability
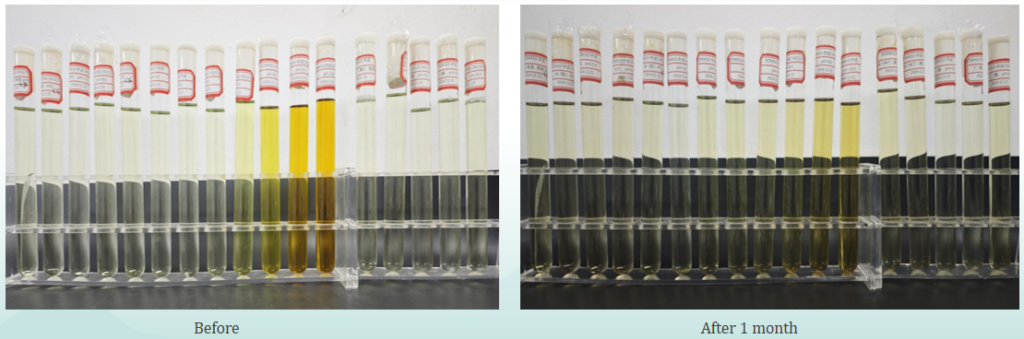
Different pH (4~10) of PMAnti-photodamage®100 due to low temperature (4 ℃), room temperature (20~30 ℃) and high temperature (45 ℃) conditions placed in 1 month. Among pH 8-10 there are obvious precipitation, solution color becomes lighter, other conditions of the color did not see obvious changes, stability is good. The rest of the group of the solution is almost no change, good stability. Therefore, it is recommended to apply pH range 4-7, placed at room temperature or low temperature.
9. Packing and Storage
Package: Packed in 25kg paper drums with two plastic bags inside.
Storage: Stored in a cool and dry place and away from direct sunlight and oxidizing agents.
10. Reference
[1]周泽琳, 杨轶眉, 顾宇翔等. 黄芩甙在化妆品中的应用研究与展望[J].日用化学品科学, 2010, 33(6):4.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7264.2010.06.007.
[2]王玉林, 何锦风, 王维民等. 某些天然植物成分防晒机理及应用[J]. 日用化学工业, 2013, 43(1):5.DOI:CNKI:SUN:CHEM.0.2013-01-019.
[3]尹慧彬.黄芩苷抑制 UVA 诱导的人皮肤成纤维细胞氧化损伤和凋亡的实验研究[D].南京医科大学,2013.DOI:CNKI:CDMD:2.1017.277321.
[4]Liu Z , Dang B , Li Z ,et al.Baicalin attenuates acute skin damage induced by ultraviolet B via inhibiting pyroptosis[J].Journal of Photochemistry & Photobiology, B: Biology, 2024, 256.DOI:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2024.112937.
[5]明亚玲,骆丹,徐晶,等.茶多酚单体和黄芩苷对紫外线辐射皮肤成纤维细胞的影响[J].中国美容医学, 2005, 14(5):4.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-6455.2005.05.008.
[6]张家安. 黄芩苷在 UVB 诱导的光老化中的作用及沉默 MicroRNA-23a 在紫外线诱导的光老化和自噬中的作用[D]. 南京医科大学, 2016. DOI:10.27249/d.cnki.gnjyu.2016.000117.
[7]骆丹 .3种中药对中波紫外线辐HaCaT细胞的干预及其机制 [J]. 中国药理学通报,2007, 23(6):6.DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-1978.2007.06.013.
[8]骆丹 , 周炳荣.紫外线皮肤光损伤及其防治的研究进展[J]. 皮肤病与性病, 2009(4):3.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-1310.2009.04.010.
[9] De Oliveira C A , Peres D D , Rugno C M ,et al.Functional photostability and cutaneous compatibility of bioactive UVA sun care products[J].Journal of Photochemistry & Photobiology B Biology, 2015, 148:154-159.DOI:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2015.04.007.
[10] Velasco MVR, Balogh T S , Pedriali C A ,et al.Rutin association with ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate and benzophenone-3: In vitro evaluation of the photoprotection effectiveness by reflectance spectrophotometry[J].Latin American Journal of Pharmacy, 2008, 27(1):23-27.DOI:10.1331/JAPhA.2008.08503.
[11] Peres D A , De Oliveira C A , Da Costa M S ,et al.Rutin increases critical wavelength of systems containing a single UV filter and with good skin compatibility[J].Skin Research & Technology, 2016, 22(3):325-333.DOI:10.1111/srt.12265.
[12] Benjamin,Choquenet,Céline,et al.Quercetin and Rutin as Potential Sunscreen Agents: Determination of Efficacy by an in Vitro Method[J].Journal of Natural Products, 2008, 71(6):1117–1118.DOI:10.1021/np7007297.
Plamed focuses on natural cosmetic ingredients for more than 10 years. We have founded four subsidiary companies, which respectively develops different kinds of cosmetic raw material. Plamed is a company whose CEO is designated as the first secretary general of Shaanxi Plant Extraction Association.
As a professional anti-photodamage natural cosmetics ingredient PMAnti-photodamage®100 manufacturer, Plamed have been constantly upgrading the production process. We firmly believe that good anti-photodamage natural cosmetics ingredient PMAnti-photodamage®100 and good anti-photodamage natural cosmetics ingredient PMAnti-photodamage®100 price will help customers make good terminal products and help customers win a lasting and broad market.













