Arbutin is a classic cosmetic raw material for skin whitening. It has been formulated in arbutin cream, arbutin serum, etc. for years. This passage mainly tells you arbutin introduction for skin from its development, category and mechanism of action.
1. Arbutin Introduction on Development
In 1989, arbutin is a herbal medicine listed in the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. Arbutin contains 5%-7.5% hydroquinone glycosides.
In 1990, Shiseido first discovered arbutin’s skin whitening effect and sold arbutin whitening serum.
In 1996, Maeda discovered that arbutin is a tyrosinase inhibitor in human Melanin cells. It has the effect for skin whitening and anti-freckle. It can effectively treat chloasma and melanoma in clinic.
In 1998, Japanese scholar Akiu et al. extracted and isolated arbutin from bearberry leaves. The skin-lightening ingredient arbutin has one more glucose molecule than hydroquinone in its structure.
In 2002, Peutaharm launched a skin lightening product with α-arbutin as the main ingredient. Shiseido and DHC also launched a series of cosmetics containing α-arbutin.
In 2004, deoxyarbutin was first mentioned in Hamed’s doctoral dissertation; and its chemical name is Phenol, 4-[(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy].
2. Arbutin Introduction on Category
Arbutin can be divided into α-arbutin, β-arbutin, and deoxyarbutin according to different molecular structures.
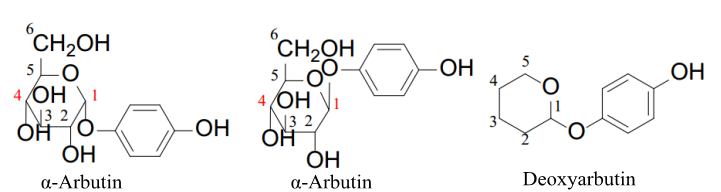
The biggest difference in physical properties between α-arbutin and β-arbutin is the optical rotation: α-arbutin is about +180°, and β-arbutin is about -60°.
Deoxyarbutin has the most effective skin whitening effect among the three. Its whitening potency is 10 times that of hydroquinone, 38.5 times that of α-arbutin, and 350 times that of β-arbutin. But deoxyarbutin is not included in International Cosmetic Raw Material Standard Chinese Name Directory (2015 Edition).
3. Comparison of Arbutins
|
α-arbutin |
β-arbutin | Deoxyarbutin | |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. | Soluble in hot water. | Excellent water solubility. |
| Heat Stability | High temperature resistant, not resistant to strong acid and alkali, ultraviolet rays. | Decompose above 50℃. | Easily decompose in aqueous solution, often exist in oil-soluble systems. |
| pH | 5.0-9.0 | 4.0-6.5 | / |
| Preparation Method | Bio-transformation. | Natural extraction. Synthetic. Bio-transformation. | Synthetic. |
| Note | The effect of inhibiting melanin production is 10 times stronger than β-arbutin. High security, narrow source and higher price. | Wider sources, lowest price, poor skin whitening effect, low security. | The effect of inhibiting melanin is 10 times that of hydroquinone, 38.5 times that of α-arbutin, and 350 times that of β-arbutin. It is not easily decomposed into hydroquinone. It is extremely unstable in aqueous solution and formulation is limited. |
From the above chart, we can see that α-arbutin is cost-effective both in skin whitening and formulation.
4. Arbutin Introduction on Mechanism
According to the structure, arbutin can be used as tyrosine analogues of tyrosinase enzyme substrates, competitively binding to tyrosinase active sites, and then inhibit tyrosinase activity. Tyrosinase is a key enzyme that can catalyze the production of melanin.
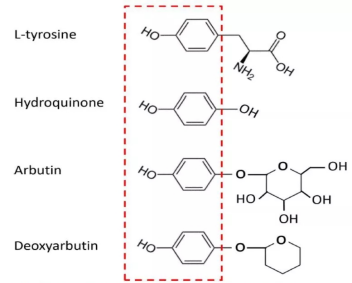
Figure. Chemical structures of tyrosine, hydroquinone, arbutin and deoxyarbutin.
Hydroquinone, arbutin and deoxyarbutin share a core phenolic moiety with tyrosine in their chemical structures, as shown in the red broken-line box.
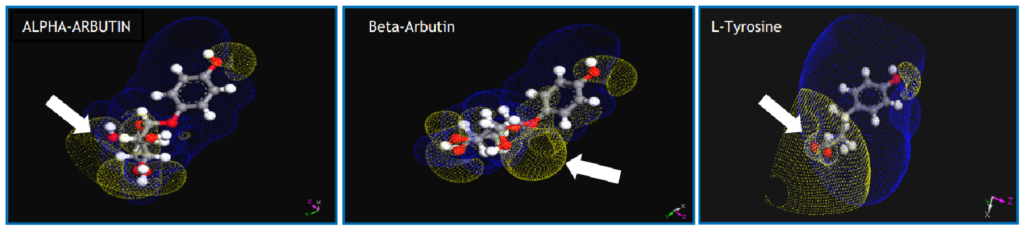 Figure. DFT (density functional theory)-optimized structure and calculated ESP’s. The yellow dots represent the negative regions and the blue dots represent the positive regions of the electrostatic potential.
Figure. DFT (density functional theory)-optimized structure and calculated ESP’s. The yellow dots represent the negative regions and the blue dots represent the positive regions of the electrostatic potential.
The excellent skin whitening effect of α-arbutin comes from its good adhesion to tyrosinase.
DFT calculates the structure and ESP (electrostatic potential) of α-arbutin, β-arbutin, and tyrosine (the substrate of tyrosinase). The result reveals the electrostatic potential of α-arbutin is similar to that of tyrosine.
The electrostatic potential of β-arbutin shows its potential difficulties when capturing tyrosinase, which means that the inhibitory ability of β-arbutin is low. In other words, it indicates that α-arbutin’s skin whitening effect is superior than β-arbutin’s.
From above arbutin introduction for skin, we can conclude that arbutin works as a competitive tyrosinase inhibitor by acting on the L-tyrosine binding site to restrain melanogenesis.Thereby arbutin achieves its de-pigmentation actions on skin. Nowadays, cosmetics ingredient arbutin has been widely applied in many skin whitening products.
Plamed aims to develop natural cosmetics raw materials. Plamed whitening ingredients are high content and low cost.
If you want to buy whitening ingredients, please contact us in following way.

Rae Wong
Mobile: +86 180 6683 3765
Email: sale@plamed.cn
Whatsapp: +86 180 6683 3765
Skype: plamed06
Wechat: 18066833765








