Vitamin C is unstable, easy to inactivity, easy to change color, and highly irritating to the skin. In order to solve the disadvantages of VC, a variety of VC derivatives have appeared one after another. The best VC derivative is Ethyl Ascorbic Acid.
Commonly used VC derivatives
We’ve summarized that the following VC derivatives are often found in common skincare products on the market today.
Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate (SAP)
Magnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate (MAP)
Ascorbyl Glucoside (Ascorbic Acid 2-Glucoside)
Ethyl Ascorbic Acid (EAA, EAC, 3-O-Ethyl Ascorbic Acid)
Ascorbyl Palmitate (AA-PAL, AA6P)
Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate (VC-IP)
Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate (SAP)
Magnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate (MAP)
Advantages:
They are a little more stable than VC ( just a little more relatively stable) and can work in a neutral aqueous solution at pH 7 with relatively little irritation. Although there are fewer skincare products that use SAP or MAP as the main whitening ingredient these days, scientists have found that SAP perform relatively well on acne.
Disadvantages:
It has to be converted into VC before it can work to whiten and lighten spots, but the absorption rate and conversion efficiency are relatively low. The overall effect of whitening and lightening is relatively poor. There is also a problem that phosphate salts need to be used under weak alkaline conditions (most VC derivatives work under acidic conditions), so sometimes it is not good to use with other ingredients, but it can be used with niacinamide.
Also it still oxidizes and yellows, but better than VC.
Suitable for people:
Introductory VC users who are not in a hurry to become whiter, people with acne.
Ascorbyl Glucoside (Ascorbic Acid 2-Glucoside)
Advantages:
Within the early players, it’s quite a bit more stable than both VC and MAP, less irritating, and active in different acidic and alkaline solutions (this is key, and it’s already possible to mix and match other ingredients at will).
Disadvantages:
Must be converted to VC before it can be, absorption and conversion efficiency is still low. Inevitably slower onset of action as well.
Suitable for people:
Beginner VC users, sensitive skin can try.
Ethyl Ascorbic Acid (EAA, EAC, 3-O-Ethyl Ascorbic Acid)
Advantages:
1. Stable, hydrophilic and lipophilic
According to the results of many studies, Ethyl Ascorbic Acid is the most stable VC derivative at present. It is also hydrophilic and lipophilic, which makes it suitable for different solvents. It can be used in both aqueous and oily solutions, which also greatly reduces the formulator’s work difficulty.
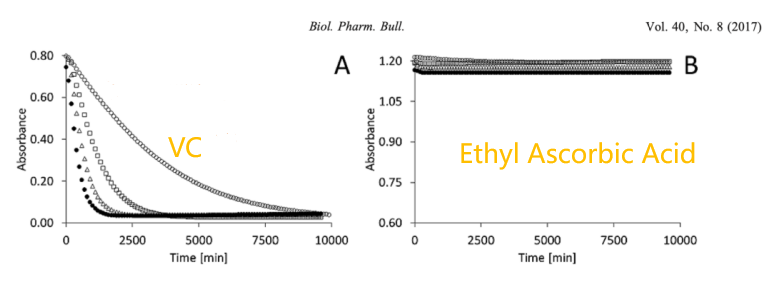
Compared to other VC derivatives, Ethyl Ascorbic Acid is ridiculously stable. After 10 days at 43℃, almost only 10% of the prototypical VC remained, whereas Ethyl Ascorbic Acid surprisingly decreased only by single digits.

2. High absorption rate
In terms of absorption rate, Ethyl Ascorbic Acid leaves VC far behind. Experiments have shown that the absorption rate of Ethyl Ascorbic Acid is almost independent of time at different temperatures (25℃, 35℃, 45℃, 55℃) (Figure B below), while the absorption rate of VC decreases dramatically.
3. High antioxidant and whitening activity
Ethyl Ascorbic Acid will have a whitening and lightening effect as long as it is added at 2% or more. Scientists tested the inhibition of various whitening ingredients on tyrosinase catalyzed oxidation of L-tyrosine into L-dopa. These include kojic acid, arbutin, VC, MAP and Ethyl Ascorbic Acid, which are five loud and clear ingredients that can’t be underestimated as long as they are added in sufficient quantities to be placed in any skincare product.
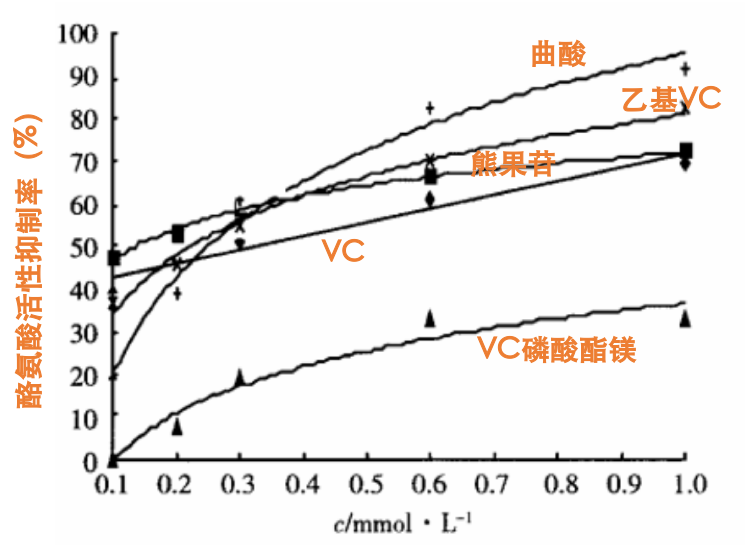 According to the results of the highest inhibition rate, kojic acid is 95.5%, Ethyl Ascorbic Acid follows at 80.8%, the VC prototype is 68.5%, and MAP is only 36.5%, which is not even half of Ethyl Ascorbic Acid.
According to the results of the highest inhibition rate, kojic acid is 95.5%, Ethyl Ascorbic Acid follows at 80.8%, the VC prototype is 68.5%, and MAP is only 36.5%, which is not even half of Ethyl Ascorbic Acid.
Besides whitening, the antioxidant capacity is equally high. Studies have shown that for the same concentration of Ethyl Ascorbic Acid and VC, the former is nearly three times more capable of scavenging DPPH free radicals than the latter (at room temperature), and there is a twofold difference in antioxidant capacity even at temperatures as high as 55℃.
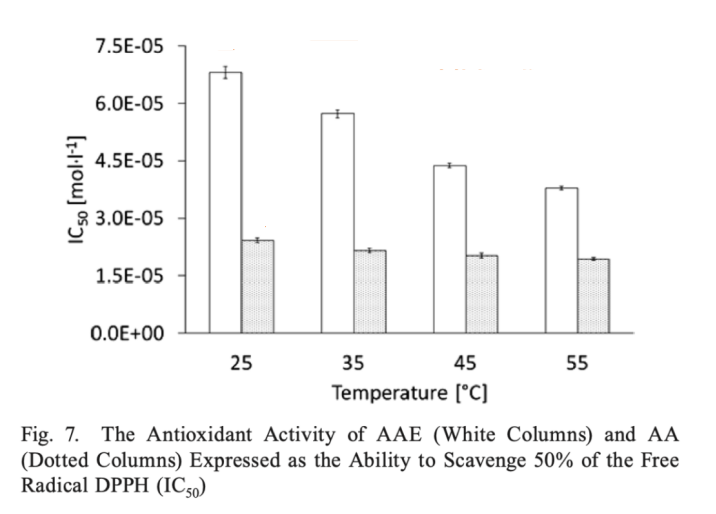 The flip side of this would be to understand that to achieve the same free radical scavenging effect, the VC must be added at a higher level than Ethyl Ascorbic Acid, which makes it more irritating.
The flip side of this would be to understand that to achieve the same free radical scavenging effect, the VC must be added at a higher level than Ethyl Ascorbic Acid, which makes it more irritating.
4. Low irritation
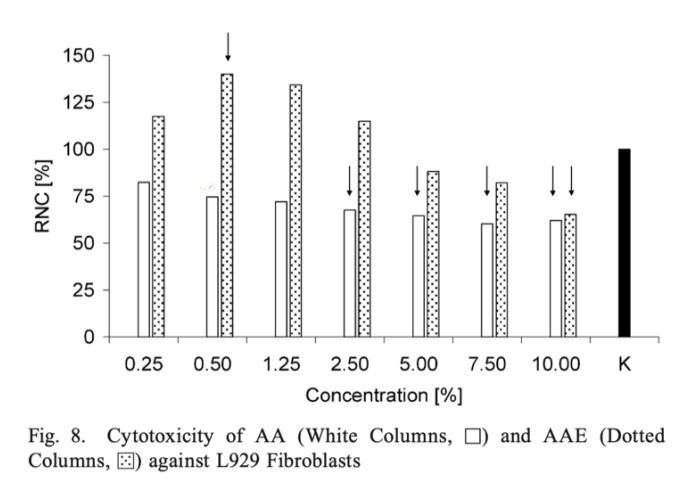
Ethyl ascorbic acid is not only highly active, but also less irritating and cytotoxic.
Ethyl Ascorbic Acid
Disadvantages:
The cost is a little higher, but currently Ethyl Ascorbic Acid has the largest shipment volume of VC derivatives, so the cost has come down.
Suitable for people:
While Ethyl Ascorbic Acid is effective, the vast majority of the population can use it, and even sensitive skin types can try it.
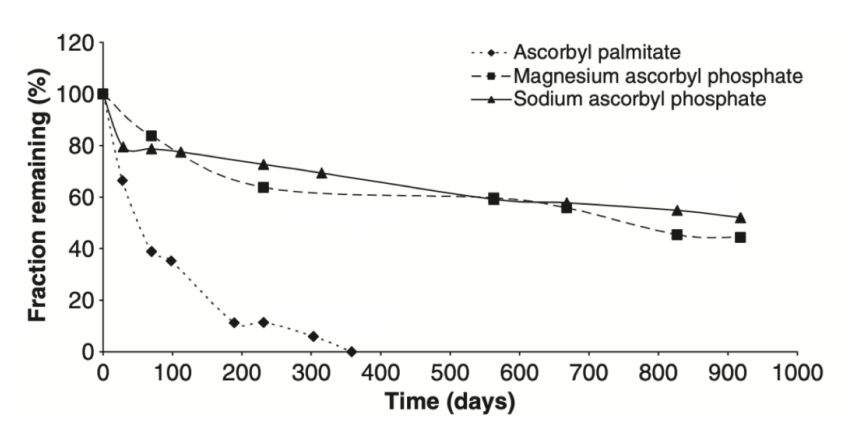
Ascorbyl Palmitate (AA-PAL, AA6P)
Advantages:
The oil solubility is very good and the skin absorption is dramatically better than several of the previously mentioned VC derivatives.
Disadvantages:
Stability is very poor, whether in a water-in-oil or oil-in-water system, it can be reduced by more than half after 14 days, and is completely miserable around 28 days.
It is also less stable than other VC derivatives, so it needs to be packaged in a way that needs to be worked on.
 Suitable for people:
Suitable for people:
It penetrates well and is less irritating, making it suitable for people who are just starting out or have sensitive skin.
Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate (VC-IP)
Advantages:
1. The lipophilicity predisposes VC-IP to much better skin penetration and absorption than VC.
2. The conversion efficiency into VC is high.
According to research results, theoretically adding 2% of VC-IP can have the effect of whitening and lightening spots. Of course as a VC derivative, the higher the content in a certain range, the better the effect of course.
Disadvantages:
Because it is an oil-soluble ingredient, it is mostly used in oils such as serum oils, which are not always suitable for oily skin.
Suit for:
People with dry skin or intolerance to ascorbic acid.
| Summary of VC and Common VC Derivative | ||||||
| Product name | Common abbreviation | Stability | Irritation | Soluble in | Effect | End products containing it |
| Ascorbic Acid | VC | Poor | High | Water | Whitening and anti-oxidation are very strong | Melano CC (Rohto)
C E Ferulic (SkinCeuticals) |
| Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate | SAP | Middle | Middle | Water | Less effective than VC, but more effective in removing blemishes | Cosmedica Vitamin C Super Serum
Amourōs Powder C 10 Serum |
| Ascorbyl Glucoside | Ascorbic Acid 2–Glucoside | Middle | Low | Water | Less effective than SAP | The Ordinary Ascorbyl Glucoside Solution 12% |
| Ethyl Ascorbic Acid/3-O-Ethyl Ascorbic Acid | EAA, EAC | High | Low | Water
Oil |
Good penetration, efficacy and VC’s similar, or even better than VC. | Hylamide C25 Stabilized Vitamin C Booster (25% Ethyl Ascorbic Acid) |
| Ascorbyl Palmitate | AA6P | Poor | Low | Oil | Good penetration, but whitening effect is not as good as VC. | Martiderm Proteos Liposome
Perricone MD Vitamin C Ester Serum |
| Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate | VC-IP | High | Low | Oil | Good penetration, efficacy is about 80% of VC. | Elizabeth Arden Vitamin C Ceramide Capsules Radiance Renewal Serum |
So Ethyl Ascorbic Acid is cosmetic formulators’ favorite VC derivative.







