Glutathione is a kind of thiol tripeptide with low molecular weight; it plays an important role in maintaining intracellular redox balance. In addition to its excellent antioxidant properties, glutathione’s anti-melanogenic properties has led to its use as a skin lightening agent. Glutathione exists in both reduced (GSH) and oxidised forms (GSSG). GSSG was superior to GSH, which is unstable in aqueous solution. GSSG ultimately produces GSH when absorbed into the skin. This article will show you glutathione whitening function for skin care.
- Glutathione Whitening Mechanism
Glutathione can reduce tyrosinase activity in three different ways. Firstly, tyrosinase is directly inhibited by chelating copper sites through sulfhydryl groups. Secondly, glutathione interferes with the cellular transfer of tyrosinase to pre-melanosomes, which are prerequisites for melanin synthesis. Third, tyrosinase inhibition is achieved indirectly through its antioxidant action. Glutathione shifts melanogenesis from true melanin to brown melanin synthesis through a reaction between sulfhydryl and dopaquinone, leading to the formation of sulfhydryl-dopa conjugates. Glutathione has a potent antioxidant capacity and has been shown to scavenge UV radiation-induced reactive oxygen species produced in epidermal cells.
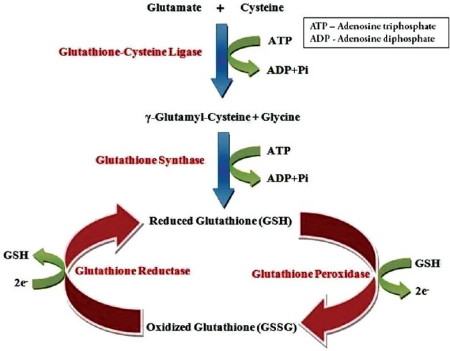
Figure. Glutathione Skin Whitening Mechanism
- Glutathione Whitening Application
The three main routes of application of glutathione for skin whitening and lightening are topical uses (creams, cleansers, lotion, etc.), oral application (capsules, tablets) and intravenous injection.
1. Topical glutathionefor skin whitening
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial in 30 healthy Filipino women aged 30-50 years provided some evidence that supports the efficacy of topical 2% Glutathione lotion in temporary whitening. Patients were randomized to take 2% Glutathione lotion and placebo lotion in two divided doses twice a day for ten weeks. Changes in melanin indices, stratum corneum moisture content, skin smoothness, skin elasticity and wrinkle formation were objectively assessed. Glutathione reduced the melanin index in a statistically significant manner compared to placebo. Glutathione is also available in the form of soaps, cleansers and creams. Also, glutathione can achieve the improvements in melasma, hyperpigmentation and skin ageing.
More product information, please visit glutathione introduction.
2. Glutathione Whitening in Oral Application
A randomized, double-blind, two-armed, placebo-controlled study in a Thai population examined the effect of oral glutathione on skin melanin indices in 60 healthy medical students. Subjects were randomized into two groups and treated with glutathione capsules at a dose of 500 mg/d, or placebo for 4 weeks. At the fourth week, there was a sustained decrease in melanin index at all six sites in the glutathione group.
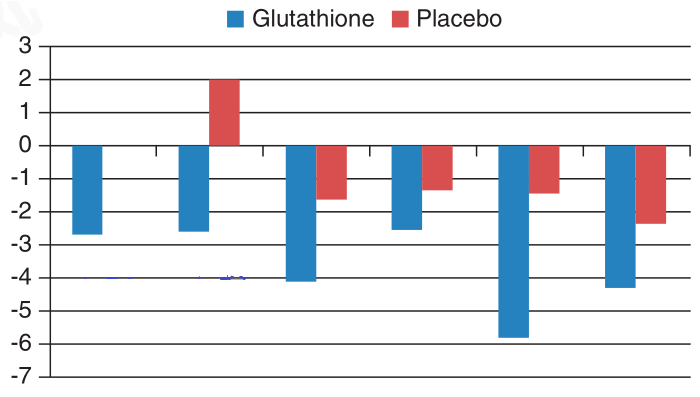
Figure. Glutathione Whitening in Oral Application
Glutathione was well tolerated. Another open study using a glutathione-containing toroches showed an improvement in skin melanin index as measured by Mexameter. They used the toroches instead of capsules to enhance and ensure stable bioavailability. The sublingual or oral route may enhance the bioavailability of glutathione more than oral tablets or capsules.
3. Intravenous Injection of Glutathione for Skin Whitening
Due to the low bioavailability of oral glutathione, intravenous injections (IV) can whiten and lighten skin instantly. A dosage of 600-1200 mg for skin lightening is recommend for IV of glutathione for once or twice a week. Although IV glutathione provides a higher therapeutic dose, which enhances its efficacy, it has a low safety due to the potential for overdose toxicity. A placebo-controlled study evaluated the whitening effect of intravenous glutathione in 32 patients. All patients were female, aged 25-47 years. 16 in group A were given intravenous glutathione and vitamin C. 16 in group B were given saline as placebo. Injections were given twice a week for 6 weeks (12 injections in total). After 12 injections of glutathione, 6 of 16 subjects (37.5%) showed significant improvement, while 3 subjects in the placebo group (18.7%) also improved. This improvement faded after discontinuation of treatment.
- Safety of Glutathione Whitening
Since glutathione is an integral part of the body’s cellular metabolism, side effects of oral supplements are expected to be mild. The US FDA and the Philippine FDA have both issued safety warnings about high-dose injections of glutathione: unapproved injections of high-dose glutathione as a skin lightener are unsafe and may damage the patient’s health with serious consequences. A single injection of glutathione should be limited to 600mg to 1200mg no more than twice a week. Adverse drug reactions reported from the use of glutathione include the following: rash, severe and potentially fatal Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis-relaxation; thyroid dysfunction; and renal dysfunction and even renal failure.
Besides glutathione whitening effect for skin care, it also has anti-oxidation, and anti-irritation effect for skin. The activity and efficacy of reduced glutathione (GSH) were more prominent in vitro in scavenging DPPH free radicals, HO free radicals and superoxide anion free radicals. When the concentration of glutathione reached 5mg/mL, the inhibition rate of hyaluronidase could reach 70.83%. In conclusion, glutathione is widely used in the field of beauty and skincare to slow down the skin aging, enhance the radiance and smoothness of the skin, repair the damaged cells, and make the skin elastic and supple, thanks to its strong antioxidant properties and special skills to inhibit the formation of melanin.







