In the last article we introduced 5 popular ingredients for skin whitening cream and their whitening mechanisms: Glabridin, Tranexamic acid, Resorcinol, Vitamin C, Glutathione. For those who are interested, you can check it out here: https://www.plamed.cn/how-to- choose-ingredients-for-whitening-cream%ef%bc%9f1/
Today, let’s see another ingredients for skin whitening cream.
Azelaic acid
Like fruit acids (extracted from various fruits) and salicylic acid (willow bark extract), azelaic acid is a naturally occurring organic acid found in plants such as cereals, wheat, rye and barley. In addition to this, azelaic acid is synthesized and secreted by the skin surface Malassezia. The azelaic acid that is now mass-produced is derived from the ozonolysis of oleic acid.
Arbutin is categorized into alpha arbutin and beta arbutin. Arbutin is able to reduce skin pigmentation and get rid of discoloration and freckles by inhibiting the activity of tyrosinase in the body and stopping the production of melanin.
Role of arbutin
- Whitening and lightening: arbutin can produce competitive and reversible inhibition of the enzyme complex, thus inhibiting the production of melanin, whitening, spot removal, skin brightening effect.
- Anti-inflammatory: arbutin was found to inhibit the degradation of proteins such as insulin in vitro test, can promote skin cell growth, help wound healing. Arbutin trace presence, the cell growth rate can be significantly increased.
- Antioxidant: arbutin has a special effect in skin care, in the repair of damaged cells at the same time can maintain their activity, with a certain anti-oxidant skin effect.
Resveratrol is a non-flavonoid polyphenol organic compounds, mainly from grapes, resveratrol, thuja, mulberries, peanuts and other plants, that is, there are some commonalities of plant polyphenols, but also has a unique biological activity.
Resveratrol has significant antioxidant and anti-free radical effects, as well as delaying aging, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and moisturizing. As one of the powerful antioxidants in nature, resveratrol is found in more than 70 species of plants, and most of the resveratrol on the market is extracted from Tiger Balm.
Role of Resveratrol
- Antioxidant
Resveratrol is a natural antioxidant that exists in plants. It plays an antioxidant role by scavenging free radicals or inhibiting the generation of free radicals, inhibiting lipid peroxidation, regulating antioxidant-related enzyme activities and other mechanisms.
- Whitening and spot reduction
Resveratrol can inhibit tyrosinase activity, especially tyrosinase in B16 cells, thus inhibiting melanin formation and ultimately achieving whitening effect.
The study below shows that compared with arbutin and ethyl Vc, resveratrol has a better inhibitory effect on tyrosinase in B16 cells.
- Anti-light aging
As shown in the table below, resveratrol can combat the problem of skin aging caused by UV radiation by increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes in photoaged skin and changing the content of oxidized products.
- Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial
Anti-inflammatory experimental studies have shown that resveratrol can achieve therapeutic effects by reducing platelet adhesion and altering platelet activity during the anti-inflammatory process. On the other hand, resveratrol has a good inhibitory effect on fungi and bacteria, and has different inhibitory mechanisms for different strains of bacteria. For example, for staphylococcus, the inhibitory mechanism of resveratrol may be to interfere with the synthesis of its cell wall, while damaging the cell membrane, it can also enter the bacterium, interfere with the synthesis of substances within the bacterium, thus affecting the growth and metabolism of the bacterium, or the two mechanisms synergistically, to achieve the effect of bacterial inhibition.
Kojic acid
Kojic acid is a naturally occurring hydrophilic fungal metabolite, a chemical product produced by fungal fermentation.
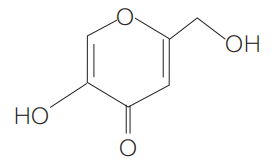 Effects of Kojic acid
Effects of Kojic acid
Inhibits tyrosinase activity:
Due to the special chemical structure of Kojic acid, it inhibits tyrosinase activity by trapping copper ions in the active site of tyrosinase, inhibiting melanin production from the source.
Kojic acid has two inhibitory effects on melanin production: on the one hand, it inactivates the hydrogenation catalyst of tyrosine required for the oxidation of tyrosine into dopa and dopaquinone; and on the other hand, it inhibits the production of 5,6-dihydroxyindolecarboxylic acid from dopa pigment.
Pterostilbene
Pterostilbene is a phenolic compound which is named after a plant of the Rosewood family of plants. Pterostilbene is one of the natural plant antioxidants, has rich medicinal value, belongs to the blood exhaust products in the antifungal active ingredients, has excellent efficacy and activity, is widely used in medicine, food, cosmetics in various fields.
Pterostilbene is a non-flavonoid polyphenolic compound derived from resveratrol by replacing two phenolic hydroxyl groups in the 3rd and 5th positions with methoxy groups, which has similar effects with resveratrol and is also known as the “second-generation resveratrol” with stronger antioxidant effects, stronger stability and higher bioavailability compared with resveratrol.
 Pterostilbene benefits:
Pterostilbene benefits:
- Antioxidant
The mechanism of action of Pterostilbene is believed to be its antioxidant properties. Pterostilbene reduces the production of oxidative stress (OS) and reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and superoxide anion (O2-), which have been implicated in the onset and pathogenesis of various disease processes. Pterostilbene has been shown to inhibit the development of malignant cells and improve normal cellular function.
- Protects against UV rays
In the research, through the cell viability test and comet assay on DNA damage analysis, it is concluded that a certain trace concentration of Pterostilbene can reduce UV damage to HFF cells.
3. Inhibit melanin
Pterostilbene has a strong ability to inhibit melanin. Pterostilbene inhibits melanogenesis by down-regulating the proteins involved in α-MSH-triggered B16-F10 cells, and induces anti-melanogenesis through autophagy.
- Anti-inflammatory
Pterostilbene purpureus can inhibit the expression of COX-2, iNOS, PGE2 and NO through the Nrf2 pathway, reducing the degree of inflammation. The presence of some destructive enzymes such as elastase and collagenase in the human body can damage the skin structure, making the skin loose and aging. Pterostilbene purpureus possesses a dual inhibitory ability, inhibiting two destructive enzymes at the same time, which can effectively anti-wrinkle and delay aging, and improve the sagging and wrinkled condition.
Panthenol
Panthenol, also known as pro-vitamin B5, is the precursor of vitamin B5 pantothenic acid. Due to the unstable nature of vitamin B5 and its susceptibility to temperature and formulation influences that reduce its bioavailability, its precursor, panthenol, is generally used in cosmetic formulations. Panthenol is more stable in nature, has better penetration and can easily penetrate the skin barrier. Panthenol is primarily used as a lubricant, emollient and humectant in cosmetics and beauty products because it adheres to the hair and can penetrate the skin to provide lubrication and moisturization.
Principle of Panthenol
Panthenol absorbed by the skin tissue, the alcohol hydroxyl group is oxidized, converted to pantothenic acid, pantothenic acid is the most important raw material for the synthesis of coenzyme A, which is an important substance in the body’s metabolism (e.g. tricarboxylic acid cycle, lipid metabolism, etc.). Therefore, the conversion of panthenol into pantothenic acid can promote the body’s protein-lipid, sugar metabolism, as well as protect the skin and mucous membranes, and improve the luster of the hair.
- Moisturizing
Panthenol’s small molecular weight allows it to effectively penetrate the stratum corneum and moisturize the skin’s surface layer with strong moisturizing effect, effectively improving skin roughness, leaving the skin soft and non-sticky.
- Repairing
Stimulate the growth of epithelial cells, accelerate the healing time of epidermal wounds, repair tissue trauma; eczema, sunburn, baby diaper rash are effective. A cream containing 5% panthenol has been documented to accelerate epidermal wound healing time by 30%.
- Hair Care
Panthenol can penetrate into the hair and moisturize the hair for a long time, improve hair shine, reduce split ends, prevent dryness, brittleness and breakage, and repair damaged hair. For nail care, Panthenol can enhance hydration to improve nail flexibility.
Niacinamide
Niacinamide was first used as a medicinal ingredient to combat pellagra and stomatitis, tongue inflammation, until 1974, when British Girish Parsad Mathur put niacinamide in sunscreen, accidentally whitening effect.
Niacinamide effects:
- Whitening and Spot Reduction
Niacinamide by inhibiting the formation of melanin particles, blocking melanin particles, skin keratinocytes between the transfer channel, accelerating the transfer of melanin in keratinocytes to the stratum corneum and promote the stratum corneum to play a whitening effect.
Below 2% of niacinamide, whitening effect are not based on accurate evidence. When the concentration exceeds 10%, the irritation may be too high. 2%-5% concentration of niacinamide is a more ideal range, with whitening function and gentle enough skin feeling.
▽ Overall skin tone brightening can be observed when using products containing 5% niacinamide for 12 consecutive weeks.
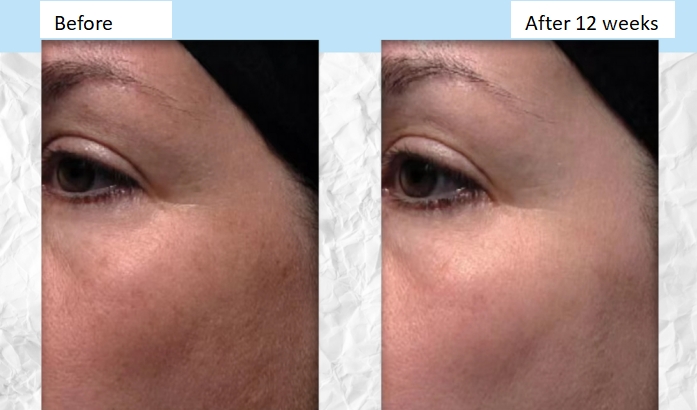
Figure source: A Review of the range of effects of niacinamide in human skin, 2002
- Repair skin barrier
Niacinamide enhances the activity of ceramide synthase and promotes ceramide synthesis in the skin. On the other hand, niacinamide can accelerate the differentiation of keratinized cells and improve the skin barrier function. And both of these can reduce skin moisture loss, strengthen the skin’s resistance to external stimuli, adding to the skin repair.
There are experiments will be 2% niacinamide cream and white Vaseline topical application on the skin of atopic dermatitis patients for comparison, twice a day for 4-8 weeks, the results found that niacinamide coated area of the TEWL (transdermal water loss) significantly reduced, while the Vaseline group has almost no change, niacinamide in the barrier damaged skin, compared with the Vaseline can be more effective moisturizing repair.
- Anti-aging
According to research, in dermal fibroblasts, niacinamide can effectively prevent glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation caused by oxidative stress, and accelerate the efficiency of mitochondria through cellular metabolism regulating factors to promote the metabolism of old cells and the generation of new cells, accelerating the skin rejuvenation.
Procter & Gamble said in the literature released in 2020 that niacinamide can promote the expression of ATG5 signaling related to autophagy in epidermal cells at pH3.8. Compared with ordinary niacinamide at pH5.8, the ability to promote cell autophagy has been increased by about 1.6 times, which accelerates the process of immune cells cleaning up the old and waste cells.
- Oil control and acne relief
Niacinamide reduces the production of fatty acids and triglycerides in sebum, which has a certain effect on oil control.
Some studies have shown that after 2% of niacinamide is used externally for 2 weeks to 4 weeks, the sebum excretion rate of yellow people will be reduced, proving that niacinamide has a certain effect on controlling the secretion of skin oil.
Ellagic acid
Ellagic acid is a polyphenol dilactone, a dimerized derivative of gallic acid. Ellagic acid is a natural polyphenol component widely found in various soft fruits, nuts and other plant tissues. It is a mild, stable and non-irritating ingredient, and is recognized as one of the effective whitening ingredients in dermatology.
Ellagic acid mechanism
- Absorption of ultraviolet radiation
Ellagic acid will be ultraviolet scanning, found that ellagic acid in the ultraviolet region are absorbed, especially 220nm ~ 300nm at the strong absorption, indicating that ellagic acid on the ultraviolet has a strong absorption, will be added to cosmetics, can avoid the skin is too much ultraviolet light, to reduce the degree of skin tanning and damage.
2. Inhibition of tyrosinase activity
There are 2 copper ions in the active site of tyrosinase, which are crucial to the activity and function of tyrosinase, and ellagic acid can chelate the copper ions in tyrosinase, so it can inhibit the activity of tyrosinase, block the formation of melanin, and effectively remove age spots and sun spots, so it is a dermatological medicine recognized as a mild whitening and lightening ingredients.
3. Reduction of melanin intermediates
The process of melanin synthesis contains a large number of oxidation reactions, ellagic acid has an antioxidant effect can restore the melanin synthesis process of various intermediates, thus blocking the formation of melanin, and ellagic acid will not cause skin sensitivity, redness and peeling, so it is more gentle than vitamin A and hydroquinone.
4. Anti-aging
Studies have proved that ellagic acid and its derivatives can strengthen the dermal-epidermal junction by increasing the proportion of type VII collagen in keratinocytes and fibroblasts, thereby reducing wrinkles, firming the skin, regulating skin texture, and slowing down the aging of the skin. Ellagic acid can effectively promote the newborn of skin elastin fibers, protect the degradation of elastin fibers protein, especially can reduce long-term or frequent radiation and sunlight in the ultraviolet radiation caused by skin tissue damage, slowing down photoaging.
Ferulic acid is a plant-derived organic antioxidant that belongs to a group of chemicals called hydroxycinnamic acids found in a variety of herbs such as Wei, Angelica, Szechuan dome, and Asclepias.
Ferulic acid is available in both cis and trans forms. The cis-type is a yellow oil, and the trans-type is a rhombohedral crystalline, white or slightly yellowish, and generally exists in the trans-type structure in nature. The trans-form structure is mainly used in cosmetics.
Ferulic acid effects
- Antioxidant
Ferulic acid is an excellent antioxidant, which is mainly due to the benzene ring connected to the hydroxyl and methoxy to make free radical chain reaction can be terminated. At the same time, it inhibits cell damage caused by hydroxyl radicals, nitric oxide and superoxide radicals, which can effectively scavenge free radicals and protect cells from oxidative damage.
The mechanism of ferulic acid’s antioxidant activity is through the reaction with free radical molecules to form stable phenoxy radicals, which makes it difficult to initiate the complex cascade reaction generated by free radicals. Ferulic acid can also act as a hydrogen donor, directly supplying atoms to free radicals and protecting cell membrane lipoic acid from oxidation.
- Whitening
According to Park et al. research ferulic acid in skin whitening, found that ferulic acid on B16F10 melanoma cells melanin synthesis and tyrosinase activity have inhibitory effect, and with the increase in the dose of the role of the more obvious, while using protein imprinting analysis shows that ferulic acid on the expression of MITF also has a significant inhibitory effect. This is the first time to prove the whitening effect of ferulic acid at the cellular level.
- Anti-inflammatory
Ferulic acid also has a certain anti-inflammatory effect. According to the study of ferulic acid for radioactive skin damage mechanism and the appropriate dose, experiments with 60Co γ-ray induced by the establishment of Wistar rat acute radioactive skin injury model, and then 5%, 10%, 15% of the ferulic acid gel for the medication. The experimental results showed that ferulic acid could inhibit the expression of NLRP3 inflammatory vesicles and realize anti-inflammatory and anti-radiation effects through the NLRP3-Caspase-1-IL-18-IL-1β pathway, which significantly reduced the radioactive skin injury.







