Glutathione (GSH) is a tripeptide composed of three amino acids (glutamic acid, cysteine and glycine). It is one of the most important antioxidants in the body and is widely found in cells, especially abundant in the liver. Glutathione’s structure is unique in that it contains a thiol group (-SH), which is key to its antioxidant function. Glutathione protects cells from oxidative damage by directly neutralizing free radicals through its thiol group or by acting as a coenzyme in a variety of antioxidant enzymatic reactions. Glutathione benefits are usually used to make oral health supplements, injections and other products, and it has a wide range of applications in the fields of medicine, cosmetics and health care.
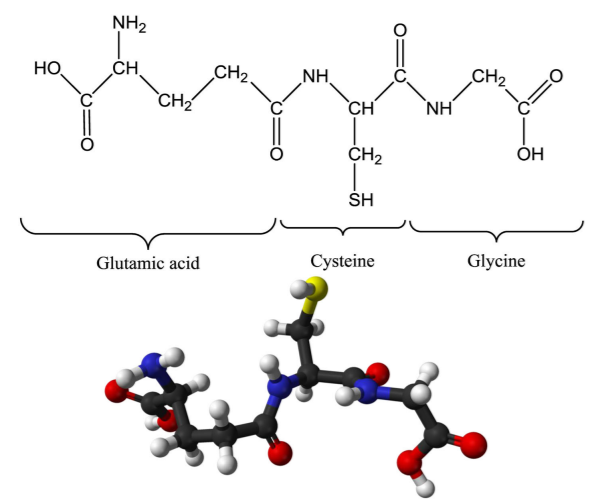
Glutathione Mechanism for Cosmetics Uses
The mechanism of action of glutathione is mainly reflected in its antioxidant effect, detoxification and immunomodulatory function. Firstly, as a potent antioxidant, glutathione can directly react with free radicals and convert them into harmless substances, thus protecting cell membranes, proteins and DNA from oxidative damage. Studies have shown that glutathione reduces hydrogen peroxide and organic peroxides to water and the corresponding alcohols in cells through the catalysis of enzymes such as glutathione peroxidase (GPx).
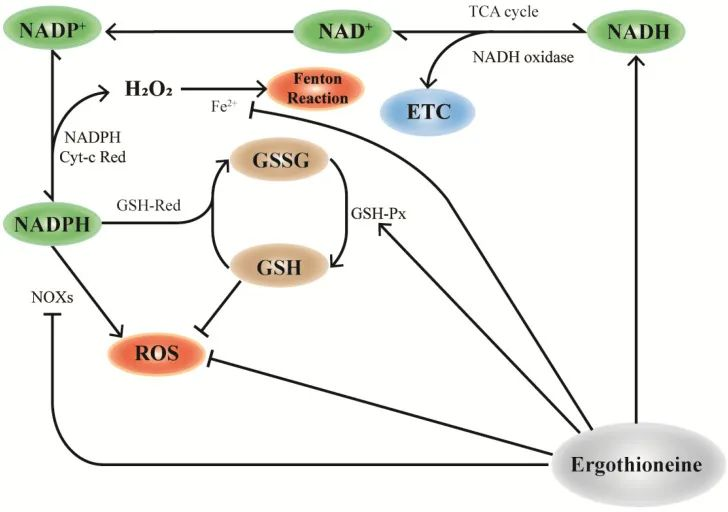 Figure. Glutathione Mechanism for Cosmetics Uses
Figure. Glutathione Mechanism for Cosmetics Uses
Glutathione Benefits for Anti-oxidation
When oxidative stress exists in the body, glutathione can play a protective role through two pathways:
- Direct scavenging of free radicals: when the skin is stimulated by the external environment such as ultraviolet rays and pollutants, free radicals and other harmful substances will be produced, leading to oxidative damage. Glutathione can react with free radicals and other harmful substances, transforming them into harmless substances and protecting cells from oxidative damage.
- Indirectly involved in the antioxidant process: Glutathione can work with other antioxidants such as vitamin C and vitamin E to enhance their antioxidant capacity and protect cells from oxidative damage.
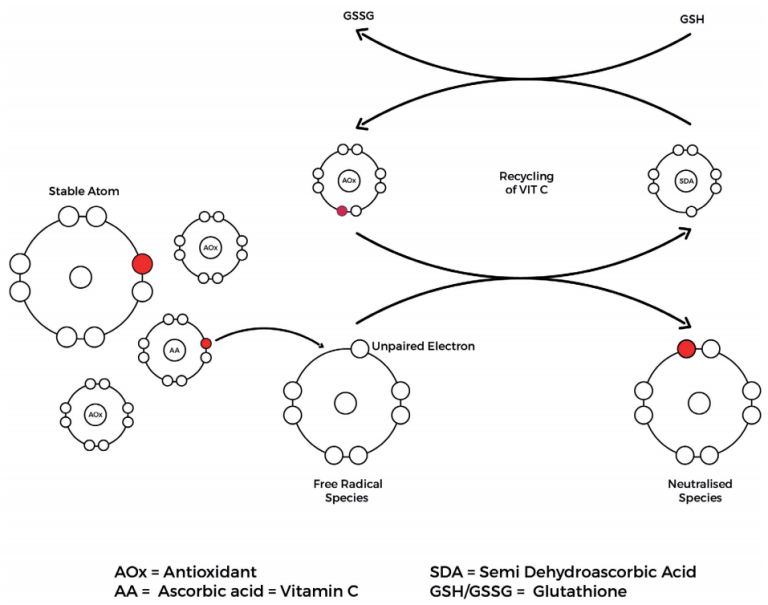
Figure. Glutathione Benefits for Anti-oxidation
Some experimental results showed that at the same concentration (0.5 mg/mL), the antioxidant performance of reduced glutathione (GSH) in scavenging DPPH radicals was at least 86 times that of oxidized glutathione (GSSG). The scavenging rate of scavenging superoxide anion radicals was 89.6% for GSH, whereas that of GSSG was 0%. And the antioxidant performance of its scavenging of HO radicals was at least 2 times that of GSSG at the same concentration (10.0 mg/mL).
Glutathione Benefits for Skin Whitening
Glutathione belongs to the group of thiol compounds that can inhibit overall melanin synthesis by binding to copper ions in the tyrosine active site to inhibit enzyme activity and by acting as an antioxidant to scavenge reactive oxygen species and free radicals.
Glutathione has the ability to reduce; in the process of melanin formation, reduced glutathione can restore the oxidized dopaquinone, converted to glutathione dopa, generating lighter brown melanin. It also inhibits tyrosinase activity, with whitening effect. Experimental data show that 1mg/ml of reduced glutathione inhibits tyrosinase activity up to 92.5%, while 100mg/ml of oxidised glutathione inhibits tyrosinase activity only up to 88.3%.
Glutathione Benefits for Anti-allergy
The in vitro and in vivo anti-allergic activity of glutathione was investigated using the hyaluronidase inhibition rate assay to study. The results showed that the inhibition rate of hyaluronidase could reach 70.83% when the concentration of glutathione was 5 mg/mL, and its inhibition effect was similar to that of 50 μg/ml paracetamol, which means glutathione had strong anti-allergic activity.
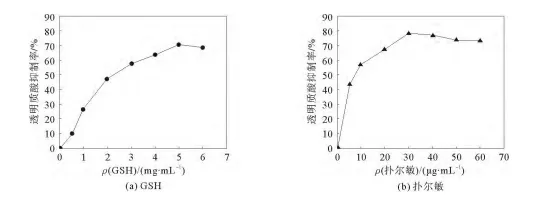
Figure. Inhibition effect of glutathione on hyaluronidase
Glutathione Uses in Cosmetics Formulation
Although Reduced Glutathione has a powerful whitening and soothing effect, its aqueous solution is extremely unstable and can only be stored for about 2 hours when exposed to air at room temperature, so we commonly see it in the form of expensive freeze-dried powders or anhydrous formulas.
The effect of different relative molecular weight of hyaluronic acid (HA) on the transdermal absorption to glutathione (GSH) has been investigated in the literature. Different relative molecular weight of hyaluronic acid (HA) have a significant effect on the amount of glutathione (GSH) medicine through the skin. With the increase of the relative molecular weight of hyaluronic acid (HA), the stronger the effect of hindering the glutathione (GSH) transdermal absorption. Comparison of the increased storage capacity of glutathione (GSH) in the stratum corneum and dermis of isolated skin by different relative molecular masses of hyaluronic acid (HA) showed that hyaluronic acid with a low relative molecular weight had the best storage capacity. Also, glutathione also had a certain transdermal absorption capacity. For glutathione to be fully effective, it is important to ensure that glutathione is retained in the stratum corneum and dermis as much as possible to achieve antioxidant and whitening effects.
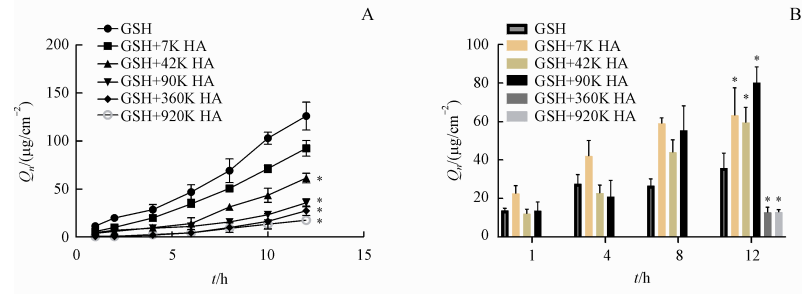
Figure. Transdermal absorption capacity of glutathione
Glutathione benefits for cosmetics uses are increasingly welcomed by market. There are many skincare products adding glutathione for skin whitening and anti-oxidation, such as LANEIGE, RNW, FILORGA, ALBION, etc..
Related Reading
- Glutathione Whitening Effect for Skin Care
- Glutathione for Skin Care in Cosmetics
- Glutathione Introduction







